Hypertension in Children
Dr Samuel Blay Nguah
Department of Child Health
Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology
Outline
- Definition
- Current outlook & risks
- BP measurement
- Diagnostic criteria for hypertension
- Investigation
- Treatment

Hypertension
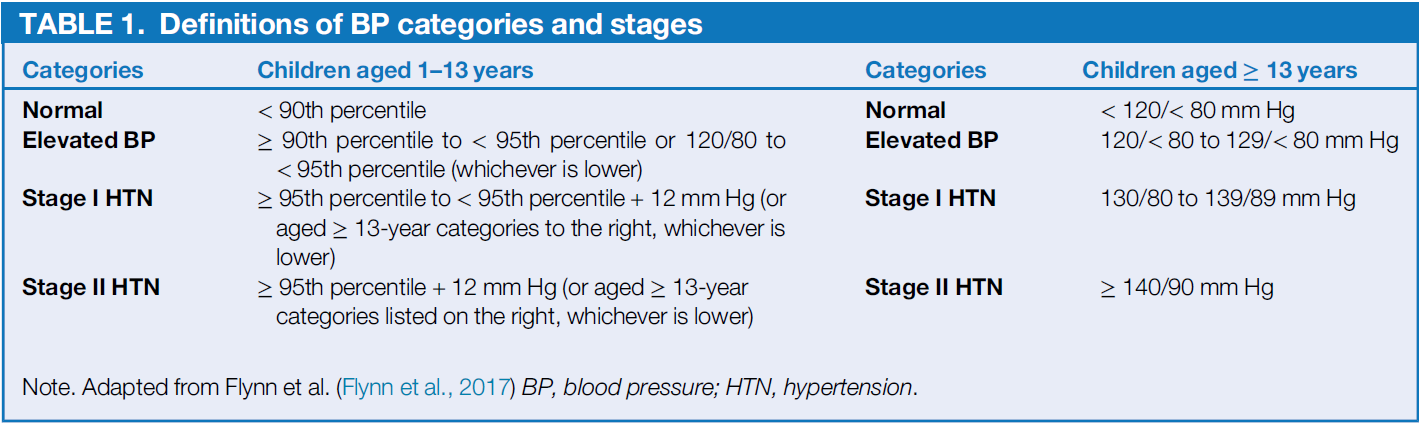
Definition (Flynn et al.,2017)
Blood pressure at or above the 95th percentile for children with the same SEX, AGE and HEIGHT.
Current Outlook
- This leads to early-onset complications of hypertension
- Increases prevalence of hypertension in adulthood
- Commoner in Black and Hispanics
- Commoner in males
- 3.5% of US children have hypertension
- Increased incidence of dyslipidemia, pre-diabetes
- Primary hypertension is now more common in the USA (esp. >6 years, obesity)

Africa/Ghana
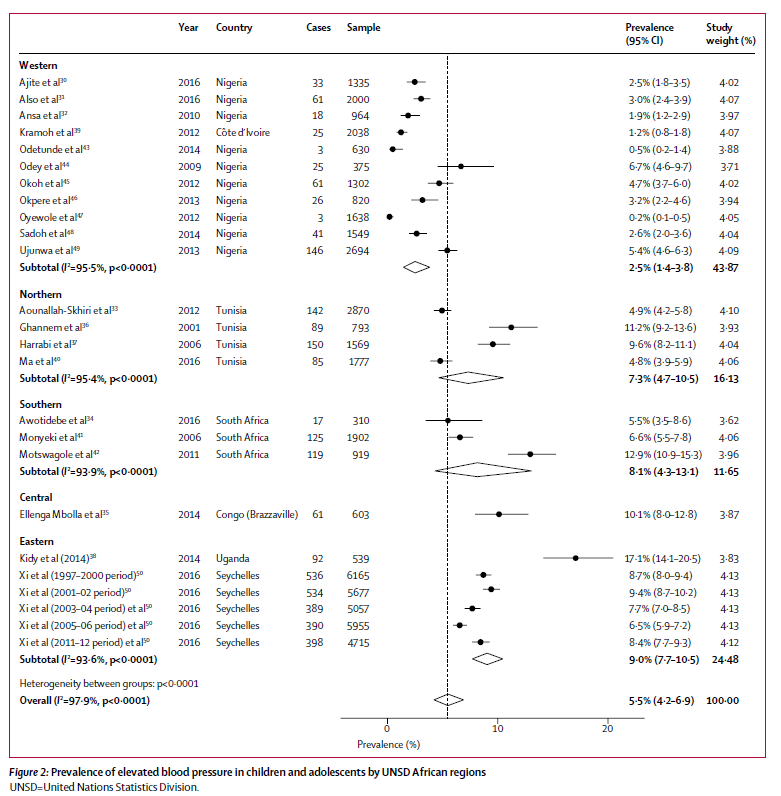
Noubiap, et. al, 2022
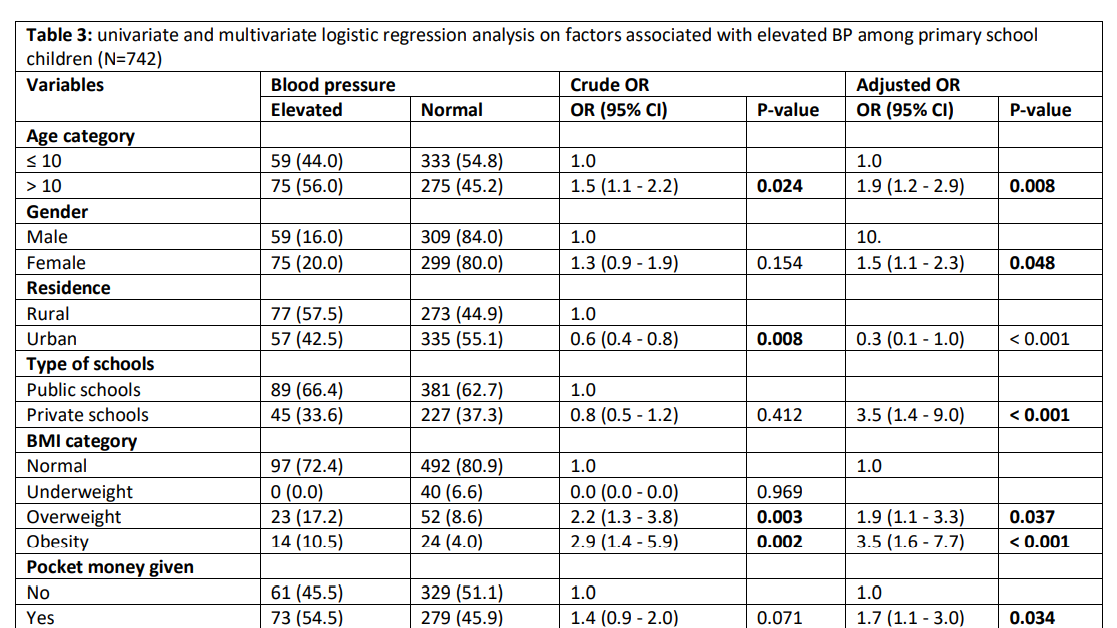
Sungwa, et. al, 2022
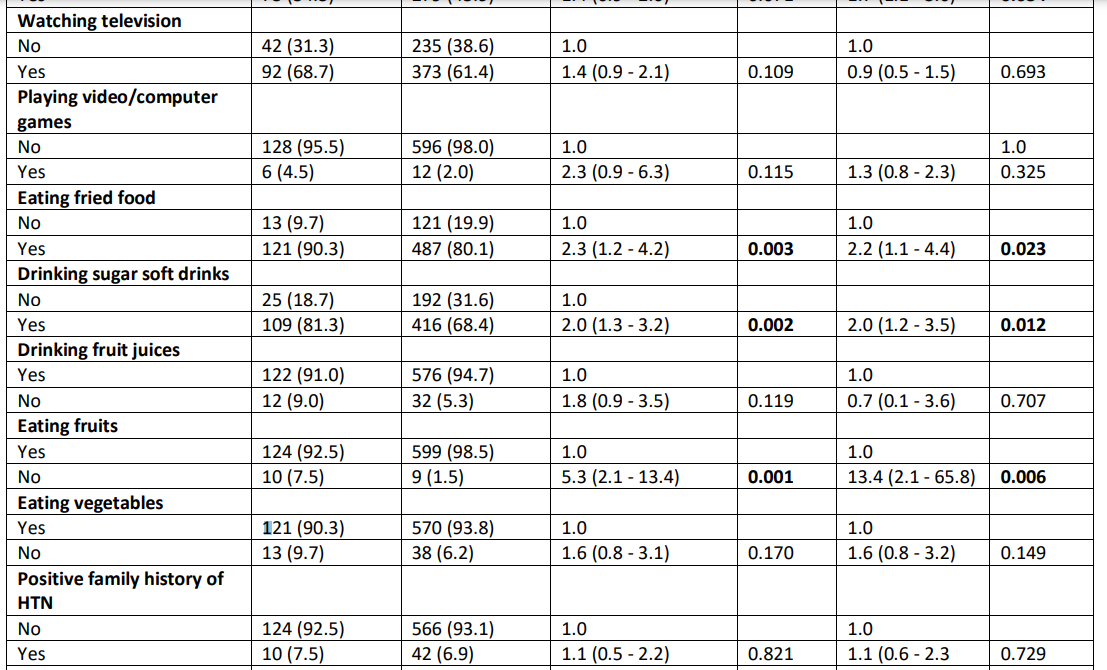
Overall, 8.5% (n = 51) of children out of the 600 had elevated blood pressure. Elevated blood pressure was significantly prevalent among obese children 18.2% (n = 12), followed by overweight 13.4% (n = 9) and the normal weight of 6.4% (n= 30) for school children (p = 0.002).
(Taiba et. al, 2022)
Guidelines…



Measuring BP
How?
- Rest for 5 mins
- Sit upright, feet on the floor
- Right arm
- Appropriate cuff size
- Bladder length = 80-100% of arm circumference
- Bladder width >= 40% of arm circumference
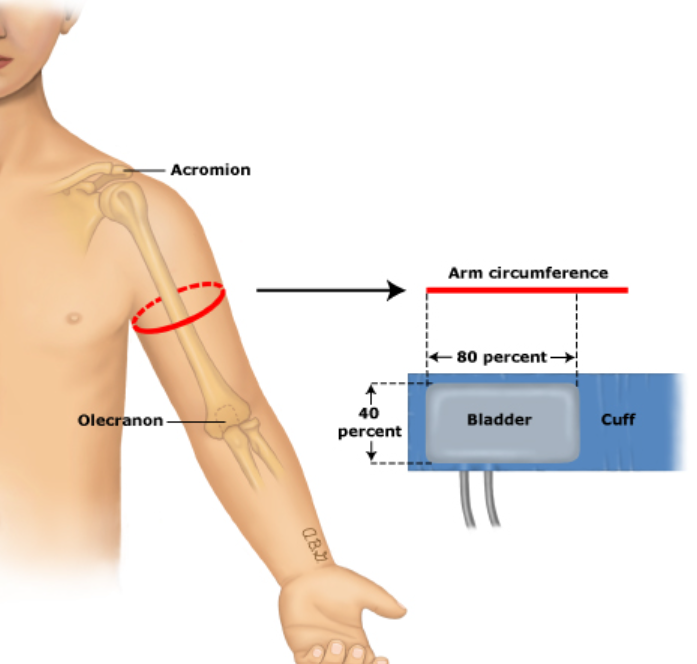
Measuring BP
Equipment?
- Auscultatory
- This is the best method
- Use K1 (Systolic) and K5 (Diastolic)
- Oscillometric
- Should be validated first
- Usually about 5-10mmHg above the auscultatory method
- Repeat with auscultatory method if > 90th percentile

Measuring BP
Who?
- > 3 years old - Yearly
- > 3 years with risk factors - Every encounter
- E.g.: Renal disease, Obesity, Diabetes, CoA, Hypertension associated medications
- < 3 years old with risks - Every encounter
- Extreme prematurity, NICU care, VLBW, CHD,
- Recurrent UTI, Hematuria, Renal disease, Family history of Renal disease, etc.
- Turner’s syndrome
Measuring BP
Procedure
- Measure the child’s height
- Determine the height centile.
- If the height centile falls between 2 centiles, use the closest centile.
- Otherwise, use the lower height centile.
- 3 measurements, average last 2
- Determine the blood pressure centile.
- Classify blood pressure using the definitions below.

Measuring BP
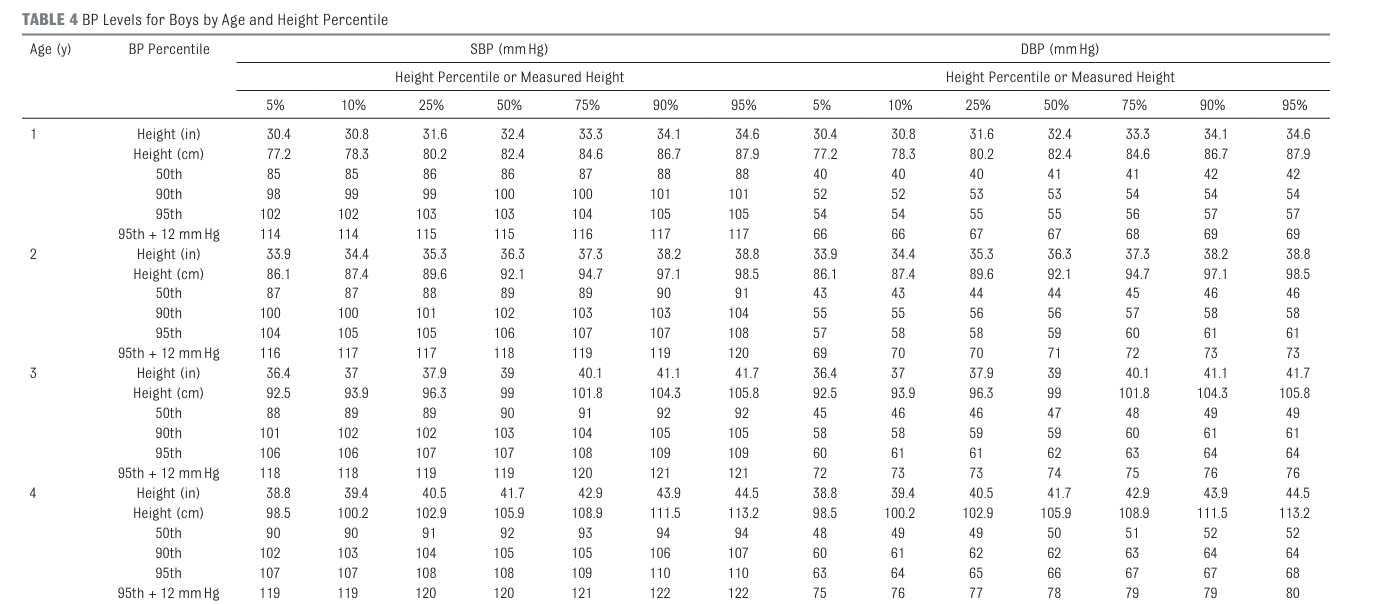
Measuring BP
Classification

What next?
Normal BP
- Measure again in a year
- Healthy lifestyle
- Low salt diet, Regular exercise, Weight control
Elevated BP
- Lifestyle modification
- Repeat 4 limbs BP in 6 and 12 months
- If still elevated BP then ABPM
Stage I
- Lifestyle modification
- Repeat in 1-2 weeks for 4 limb BPs
- Repeat in 3 months
- If elevated, ABPM ± Drug treatment
What next?
Stage II
- 4 limb BPs check
- Should repeat in 1 week, within which ABPM ± Drug treatment ± Other investigations
Greater than 13 years
- Repeat BP at the same visit
- Classify accordingly
Emergency referral
- Symptomatic
- Stage II hypertension
- BPs >30mmHg above 95th percentile in children or
- >= 180/120mmHg in adolescents
- They have a high risk of hypertensive emergency
Clinical evaluation
History & Examination
- Associated symptoms
- Chronic Headache, tinnitus, visual disturbance, etc
- Possible cause of hypertension
- Renal: UTI,
- Cardiac: Palpitation, easy fatiguability, etc
- Metabolic: Cushing’s syndrome, etc
- Medications: Steroids, NSAIDs
- Genetic disorders - William’s syndrome, Turner’s syndrome
- Possible cause of hypertension
- Newborn issues: Prematurity, Low birth weight, maternal hypertension, etc
- Endocrine: Hyperthyroidism, Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, etc
- Nutritional: Obesity, Overweight, Increased salt intake
- Oncoligcal: Phaechromaocytoma, Neuroblastoma
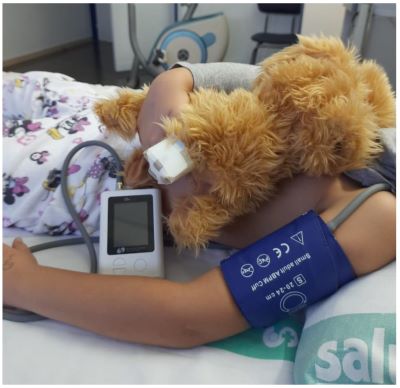
Ambulatory BP Monitoring
- Measures every 20-30mins for 24 hours
- Improved accuracy
- A better predictor of end-organ damage
- Diurnal variation in BP
- Assess nocturnal dipping
- Better reflect daily BP status
Laboratory
All hypertensives
- Electrolytes
- Blood urea nitrogen and creatinine
- Urinalysis
- Lipid profile
Obese hypertensives
- Fasting lipid profile
- Hemoglobin A1C
- AST, ALT
Others
- Based on the clinical presentation
- Echocardiogram to determsine
- End organ damage & for follow-up
Therapy
Goal
- BP < 90th percentile OR
- BP < 130/80 mmHg
Assymptomatic
- Healthy diet
- Low salt, oils, sweetened-beverages
- Lean protein source: meat, fish, legumes, etc
- Veges, fruits
- Regular exercise (3-5 days a week, 30-60 minutes)


Pharmacological Therapy
Who?
- 6 months after lifestyle changes
- Symptomatic
- Lack of modifiable factors
- Stage II
- Chronic kidney disease
- Diabetes mellitus
What?
- Long-acting (once-daily medication)
- Maximise dosage over 2-4 weeks before adding on
- Consider underlying conditions
- ACE-I and ARBs
- Beta-blocker
- Calcium channel blocker
- Diuretic
- Others (methyl dopa, etc)
Combining drugs

Take home
- Hypertension in children is commoner than we think
- All children > 3 years should be screened yearly for hypertension
- Let’s preach and practice a “Healthy Lifestyle”

Thank you! 🙏


Hypertension in Children Dr Samuel Blay Nguah Department of Child Health Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology